Embarking on a journey into the intricate world of parasites, this blog post aims to shed light on these often misunderstood organisms. Understanding parasites is crucial for maintaining optimal health. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the types of parasites, their impact on the body, and natural approaches to prevention and cleansing.
Types of Parasites: Unveiling the Diversity
-
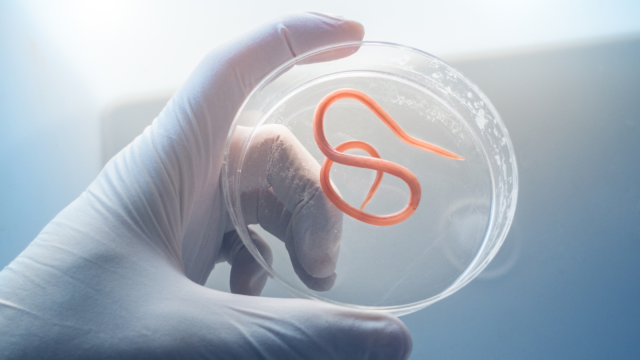
Intestinal Parasites: Common intestinal parasites, including roundworms, tapeworms, and protozoa.
-
- Roundworms (Nematodes):
- Overview: Roundworms are a type of helminth, a group of parasitic worms. They are cylindrical in shape and can vary in size. Some common types include Ascaris lumbricoides.
- Transmission: Infection often occurs through the ingestion of contaminated food, water, or soil containing roundworm eggs. Poor hygiene practices can contribute to transmission.
- Symptoms: Symptoms may include abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, and visible worms in stool. In severe cases, roundworm infections can lead to malnutrition.
- Tapeworms (Cestodes):
- Overview: Tapeworms are flat, ribbon-like worms that inhabit the intestines. Different species affect humans, such as Taenia saginata (beef tapeworm) and Taenia solium (pork tapeworm).
- Transmission: Consumption of undercooked or raw meat containing tapeworm larvae is a common mode of transmission. Poor food handling practices can contribute to infection.
- Symptoms: Symptoms may include abdominal discomfort, weight loss, and the passage of tapeworm segments in stool. Some individuals may remain asymptomatic.
- Protozoa:
- Overview: Protozoa are single-celled organisms that can cause various intestinal infections. Common intestinal protozoa include Giardia lamblia and Entamoeba histolytica.
- Transmission: Contaminated food or water, as well as person-to-person contact, can lead to protozoan infections. Poor sanitation is a significant factor.
- Symptoms: Symptoms vary but may include diarrhea, abdominal cramps, nausea, and fever. Protozoan infections can be chronic and may lead to complications if untreated.
Understanding these parasites is crucial for recognizing symptoms and seeking timely medical attention. Diagnosis often involves laboratory tests to identify the specific parasite and guide appropriate treatment. It’s important to note that maintaining good hygiene, practicing safe food handling, and ensuring the cleanliness of water sources are key preventive measures against these intestinal parasites. If individuals suspect they have a parasitic infection, consulting a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment is recommended.
- Roundworms (Nematodes):
-
-
External Parasites:Parasites affecting the skin and hair
-
Parasites affecting the skin and hair can cause a range of dermatological conditions. Here are a few examples of such parasites:
- Scabies (Sarcoptes scabiei):
- Overview: Scabies is a contagious skin infestation caused by the mite Sarcoptes scabiei. These microscopic mites burrow into the skin, causing intense itching and a characteristic rash.
- Transmission: Close personal contact is the primary mode of transmission. The mites can spread easily in crowded living conditions.
- Symptoms: Symptoms include intense itching, especially at night, along with a pimple-like rash and small burrow lines on the skin. Scratching may lead to secondary bacterial infections.
- Head Lice (Pediculus humanus capitis):
- Overview: Head lice are tiny insects that infest the scalp and hair. They feed on blood and lay eggs (nits) on hair shafts.
- Transmission: Direct head-to-head contact is the most common way lice are transmitted. Sharing personal items like combs, brushes, or hats can also contribute to infestations.
- Symptoms: Itching of the scalp is a primary symptom. The presence of nits (tiny white or yellowish oval eggs) attached to hair shafts is a characteristic sign.
- Ringworm (Dermatophyte Infections):
- Overview: Ringworm is not caused by worms but by fungi known as dermatophytes. Different species can affect the skin, nails, and scalp.
- Transmission: Direct contact with an infected person, animal, or contaminated surfaces can lead to ringworm infections.
- Symptoms: Ring-shaped red or silvery patches on the skin, along with itching and scaling, are common symptoms. In the scalp, it may cause hair loss and scaling.

- Body Lice (Pediculus humanus corporis):
- Overview: Body lice are similar to head lice but infest clothing and bedding. They feed on blood and move to the skin to feed.
- Transmission: Close contact with infested individuals and sharing of infested clothing and bedding can lead to body lice infestations.
- Symptoms: Itching, red bumps, and visible lice or eggs on clothing are characteristic signs of body lice infestations.
- Fleas:
- Overview: Fleas are parasitic insects that commonly infest the fur of animals but can also bite humans.
- Transmission: Fleas can be transmitted to humans from infested pets or through contact with infested environments.
- Symptoms: Itchy, red, raised bumps on the skin, often in clusters, are typical symptoms of flea bites. Scratching can lead to secondary infections.
Treatment for skin and hair parasites typically involves topical or oral medications prescribed by healthcare professionals. Proper hygiene practices, regular cleaning of personal items, and avoiding close contact with infested individuals or environments are essential preventive measures. If someone suspects a parasitic infestation, seeking prompt medical attention is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
- Scabies (Sarcoptes scabiei):
-
The Impact of Parasites on Health: Understanding the Signs

- Digestive Disruption:
-
Parasites can significantly impact the balance of the gut microbiome, leading to a variety of digestive issues and potential long-term consequences. The gut microbiome is a complex ecosystem of trillions of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites, that inhabit the gastrointestinal tract. When parasites disrupt this delicate balance, it can result in several negative effects:
- Dysbiosis:
- Parasitic infections can contribute to dysbiosis, an imbalance in the composition and function of the gut microbiome. This imbalance may involve a decrease in beneficial microorganisms and an increase in harmful or pathogenic species.
- Inflammation:
- Parasites may trigger an inflammatory response in the gut as the body’s defense mechanism. Chronic inflammation can disturb the microbial balance, impacting the diversity and abundance of beneficial bacteria.
- Altered Immune Response:
- The presence of parasites can affect the immune response in the gut. An overactive or suppressed immune system can lead to imbalances in the gut microbiome, influencing the abundance of different microbial species.
- Nutrient Absorption:
- Parasites may interfere with nutrient absorption in the intestines. Some parasites consume nutrients meant for the host, leading to malabsorption and nutrient deficiencies. This can affect the availability of nutrients that support the growth and maintenance of beneficial gut bacteria.
- Mucosal Barrier Disruption:
- Parasites can damage the mucosal lining of the intestines, compromising the integrity of the gut barrier. A compromised barrier allows harmful substances to enter the bloodstream, triggering immune responses and further contributing to dysbiosis.
- Production of Toxins:
- Some parasites release toxins as part of their life cycle. These toxins can have detrimental effects on the gut microbiome and the overall health of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Alteration of Short-Chain Fatty Acid Levels:
- Parasites may impact the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which are essential for maintaining gut health. Changes in SCFA levels can affect the growth and activity of beneficial bacteria.
- Shift in Microbial Metabolites:
- Parasitic infections can lead to changes in the production of microbial metabolites, influencing the overall metabolic environment in the gut. This shift may have consequences for both the host and the microbial community.
Addressing the impact of parasites on the gut microbiome involves not only eliminating the parasites through appropriate medical treatment but also restoring and supporting the balance of the microbiome. Probiotics, prebiotics, and dietary interventions aimed at promoting a diverse and healthy microbial community can be important components of the recovery process. Additionally, maintaining good hygiene practices and taking preventive measures can help reduce the risk of parasitic infections and their impact on the gut microbiome.
Symptoms like bloating, gas, and irregular bowel movements caused by Parasites:
- Dysbiosis:
-
Bloating: Bloating is a common symptom associated with parasitic infections affecting the digestive system. Parasites can disrupt the normal functioning of the intestines, leading to an accumulation of gas and fluid. As parasites interfere with the absorption and digestion of nutrients, the gut may become inflamed, causing a feeling of fullness and abdominal discomfort. Bloating may be particularly noticeable after meals, and persistent or recurrent bloating should prompt further investigation for potential parasitic involvement.
- Gas: Increased gas production is another symptom that may arise from parasitic infections in the gastrointestinal tract. Parasites can alter the balance of the gut microbiome, leading to the overproduction of gases such as methane and hydrogen during the breakdown of undigested food. Excessive gas can result in abdominal distension, discomfort, and flatulence. Monitoring changes in gas patterns, especially if accompanied by other digestive symptoms, can be indicative of a potential parasitic infection.
- Irregular Bowel Movements: Parasitic infections can disrupt the normal patterns of bowel movements, leading to irregularities in frequency and consistency. Some individuals may experience diarrhea, characterized by loose or watery stools, while others may develop constipation with difficulty passing stools. The presence of parasites in the intestines can irritate the lining, triggering changes in bowel habits. Monitoring variations in bowel movements and noting persistent irregularities can be essential in recognizing and addressing potential parasitic infections. Individuals experiencing persistent bloating, gas, or irregular bowel movements should seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
-
-
Beyond the Gut:
Parasites can have broader health implications beyond the digestive system, and one significant aspect is their impact on nutrient absorption. Here’s an exploration of how parasites can contribute to nutrient absorption issues and affect overall health:
- Malabsorption:
- Parasites can interfere with the normal absorption of nutrients in the intestines. They may compete with the host for essential nutrients, leading to malabsorption. This can result in deficiencies of vital nutrients like vitamins, minerals, and proteins, affecting various physiological processes.
- Nutrient Depletion:
- Parasites may consume nutrients meant for the host, causing a depletion of essential substances necessary for maintaining health. This can lead to fatigue, weakness, and a compromised immune system as the body lacks the necessary building blocks for optimal functioning.
- Iron Deficiency Anemia:
- Some parasites, such as hookworms, can cause chronic intestinal bleeding, leading to iron deficiency anemia. Iron is crucial for the formation of red blood cells and oxygen transport in the body. Anemia can result in fatigue, weakness, and overall decreased well-being.
- Vitamin Deficiencies:
- Parasites may impact the absorption of specific vitamins, such as vitamin B12 and vitamin A. Vitamin B12 is essential for nerve function and red blood cell formation, while vitamin A is crucial for vision, immune function, and skin health. Deficiencies in these vitamins can lead to a range of health issues.
- Protein Loss:
- Some parasites can cause protein-losing enteropathy, a condition where proteins are lost through the intestines. Proteins are essential for numerous bodily functions, including immune response, tissue repair, and enzyme production. Protein loss can contribute to muscle wasting, edema, and a compromised immune system.
- Weight Loss and Stunted Growth:
- Chronic parasitic infections, especially in children, can lead to weight loss and stunted growth. The nutritional depletion caused by parasites can hinder normal growth and development, impacting overall physical and cognitive well-being.
- Immune System Modulation:
- Parasites have evolved mechanisms to modulate the host’s immune response. While this helps the parasites evade detection, it can also result in an altered immune system that may contribute to increased susceptibility to other infections and immune-related disorders.
Addressing the broader health implications of parasitic infections involves not only eliminating the parasites but also addressing the nutritional deficiencies and health issues they may have caused. Proper medical diagnosis, treatment, and nutritional support are essential in restoring optimal health and well-being. Individuals experiencing symptoms or concerned about potential parasitic infections should seek professional medical advice for timely intervention and appropriate management.
- Malabsorption:
Conclusion:
Unveiling the World Within Parasites
In the journey through the intricacies of parasites and their impact on health, we’ve explored how these organisms can disrupt the delicate balance of the gut microbiome, contribute to nutrient absorption issues, and affect various aspects of well-being. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of parasitic infections is a crucial step in taking control of one’s health.
Invitation to Our Next Blog: Empowering Your Body: A Comprehensive Guide to Natural Parasite Prevention
To further empower you on your wellness journey, we invite you to explore our next blog, where we will delve into natural remedies for parasite prevention. In this upcoming discussion, we’ll focus on:
- Herbs with Anti-Parasitic Properties:
- Highlighting natural ingredients known for their effectiveness against parasites.
- Providing insights into incorporating these herbs into your daily life.
- Colon Cleansing:
- Discussing the role of colon cleansing in preventing and eliminating parasites.
- Introducing natural methods and practices for maintaining a healthy colon.
- Signs You Might Have Parasites: A Closer Look at Symptoms:
- Exploring gastrointestinal and non-gastrointestinal symptoms.
- Providing guidance on when to seek professional help.
- Preventive Measures: Adopting a Holistic Lifestyle:
- Emphasizing hygiene practices to prevent parasitic infections.
- Offering practical tips for maintaining a clean and healthy environment.
- Dietary Habits:
- Discussing dietary practices that support a hostile environment for parasites.
- Highlighting foods that promote digestive health and immunity.
Taking Control of Your Health
In our continuous effort to provide valuable insights, this upcoming blog will offer actionable steps and natural solutions to enhance your body’s defenses against parasites. Stay tuned as we explore empowering practices that contribute to a healthier, parasite-free life. Your journey to optimal well-being continues with knowledge, awareness, and the proactive steps we’ll explore together in our next discussion.

